Albert Einstein
IQ 190
Albert Einstein was without question the most influential physicist of the 20th Century as the Father of Modern Physics, who sparked the scientific revolution with his groundbreaking discoveries and work. Two of Einstein's notable contributions are The General Theory of Relativity, which provided a coherent explanation for gravity as an intrinsic geometric property within space-time geometry, and The Photoelectric Effect, which established QuantumTheory within Physics.
Albert Einstein was revered as one of the foremost scholars in Physics. Through this article, discover more about Albert Einstein's IQ and life.
I. What is Albert Einstein's IQ?
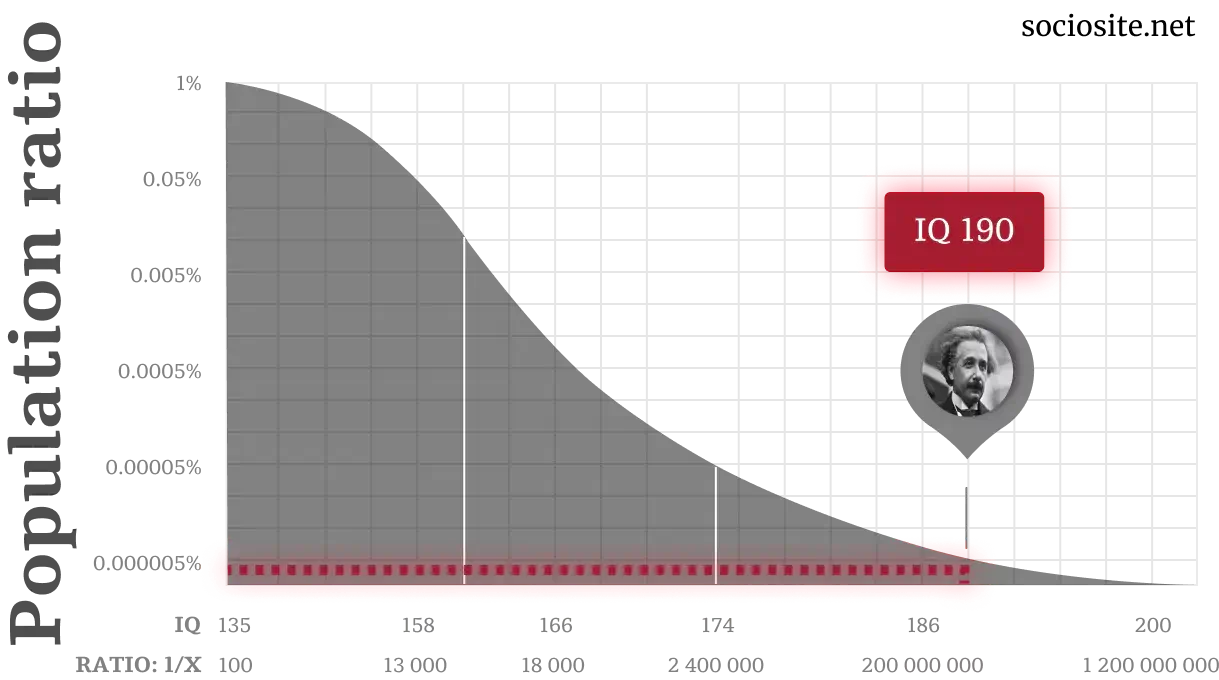
Albert Einstein never undertook any standard IQ test; therefore, his actual IQ is not definitively ascertainable. However, experts have taken it upon themselves to analyze his IQ, and as per such postulations, his IQ is approximately between 160 and 190, which lies within the typical range for such estimates. Born in 1879 in Germany, this man is famously known for formulating the theory of relativity. This theory coexists with quantum mechanics and forms the base of modern physics. He also made a contribution to fission theory and provided base knowledge for further development in the making of nuclear weapons. He finally died in 1955 due to a rupture of the aorta because he had a saccular aneurysm that had been diagnosed.
Throughout his life, Einstein wrote more than 300 scientific papers. He received various honors, including the Max Planck Medal, the Copley Medal, and the Nobel Prize in Physics, and he was proclaimed Time magazine's Person of the Century. Such was the contribution of Einstein that even now, quite often his work is generalized under the name “genius.”
II. Albert Einstein IQ and his life
Albert Einstein was one of Hermann and Pauline Einstein's two children. He was born in Ulm, in the Kingdom of Württemberg, to Hermann and Pauline Einstein, and his younger sister was Maja Einstein. Soon after, the family relocated to Munich, where their father joined his uncle to establish Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a company specializing in the production of direct current electrical equipment.
Albert Einstein had an extremely high IQ, but as a child, he was slow to speak. His parents were so concerned that they took him to a doctor. He later recounted, "They were terrified when I needed one." Even after he began speaking around the age of two, he developed some speech habits that led family members to call him an "idiot".
Einstein intensely disliked authority figures; once, his principal expelled him for being too conservative at school. Yet these very same characteristics of Einstein contributed to his genius - his stubborn nature led to asking very intelligent questions of them. At the same time, slow speech enabled him to take in and understand details people took for granted. At age 5, his father gave him a compass, which became his lifelong fascination: magnetic fields being at the heart of all this discovery!
1. Albert Einstein's IQ Intelligence and Education Background
At five, Albert attended Catholic Elementary School as his initial educational experience. He later moved on to Luitpold Gymnasium after three years, until finally leaving Germany after finishing advanced primary and secondary education. Within months of beginning formal mathematics classes at Luitpold Gymnasium at age seven, Einstein displayed early indications of aptitude and skill for mathematics through mechanical model-building exercises meant only as games or amusement. However, after Max Talmud gave him popular science books, including mathematical texts as well philosophical writings, around age ten, this interest began to blossom into passions that became truly extraordinary.
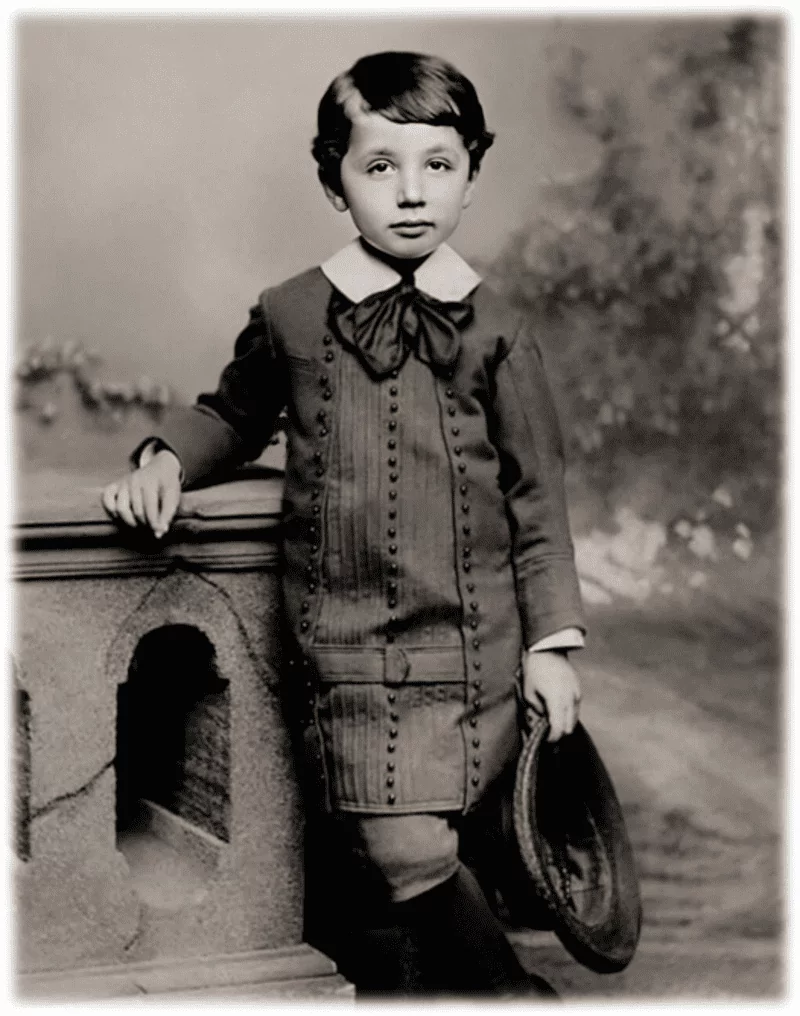

1884 , GERMANY : The celebrated genius scientist and physicist ALBERT EINSTEIN (5 years old).
From 1895 to 1896, Einstein pursued his secondary education at the Aargau Cantonal School in Aarau, Switzerland on the advice of the head of the Zurich Polytechnic. The fear of being compelled by military conscription to render service made Einstein in 1896 renounce his Wurtemberg citizenship outright, passing an examination that September with the highest marks on a mathematics paper and physics paper and an average of overall merit. Thereafter, at the age of 17, he registered for the mathematical and physics Teaching Diploma Course of the ETH Zurich and was admitted in a year that saw him attain citizenship.
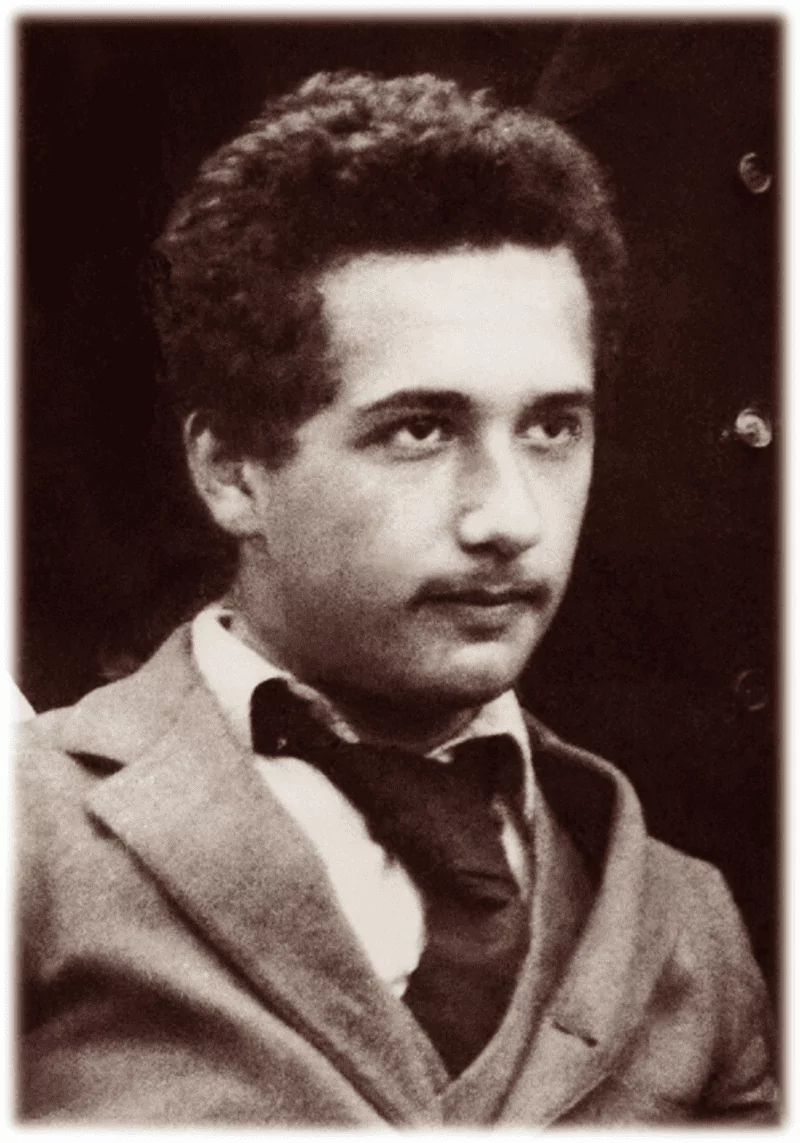

Albert Einstein (17 years old) as a young man in 1896.
2. Albert Einstein IQ and his successful Career
a. Academic Career
Doors were opening academically for Albert Einstein. In 1910, he was a lecturer in Bern and within a year he became an associate professor in Zurich; and soon after this full professorships came his way at Prague and then again Zurich before coming full circle home, where is academic trip finally attained the status of a professor at Berlin’s Institute for Mathematics – Prussian Academy of Sciences Fellowship status being conferred upon him in Berlin in 1912.
He took the position of an ordinary member of the faculty at the University of Berlin but never lectured there and yet enjoyed the full professor’s salary, thereby enabling him to devote all his time and attention to formulating and working on a theory. He also held the post of Director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics until the early thirties; Einstein even went through a formal registration as a student therein.
b. In World War I
By the above, Einstein has emerged as a staunch critic and pacifist against the strongly nationalistic German nationalistic ideologies during the First World War. As many as 93 leading German scientists, artists, and academics who had backed Germany during World War I gave their signatures in support of a wartime manifesto. Einstein boycotted the invitation to sign by publishing a counter-manifesto deploring Germany’s participation. Einstein was a German through World War I and yet the effects of it seem not to have mattered much in his academic and professional life. It is during the First World War that Einstein came out with his greatest scientific discovery: General Theory of Relativity; often its accomplishment is called his magnum opus and must have added much to Albert Einstein’s academic IQ all through that confrontation.
c. World Traveler
Instantly after World War I, Einstein became an overnight sensation when experiments during the eclipse in 1919 confirmed his Theory of General Relativity by reflecting starlight. Universities and academics from around the world invited him to lecture on his breakthrough theories in their countries — many to the extent that they had invited him several times in 1921-1923 alone! Between these lectures, he had meetings with scores of world dignitaries, including King Juan Carlos of Spain, Emperor Meiji of Japan, and President Harding of the United States, and the delegates he met, headed by King Juan Carlos himself!
d. Awards and Achievements
Einstein’s theory of special relativity revolves around the relativity of time and space to a reference frame of an observer; its major paradox lies in this notion of the constant speed of light, which led to one of the many amazing paradoxes of his work: the length contracts on moving toward the speed of light. At the same time, mass is increased, and over time, mass and energy are considered equivalent.
In the year 1916, Albert Einstein published the general theory of relativity and was awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for this specific work, and as well as his 'contributions to the domain of theoretical physics.' His attainment of such success can, therefore, not only be pinned on high IQ but determination and dedication to science that saw him scoop all these honors and prizes for himself.
- Einstein first joined the Prussian Academy of Sciences as a full member on November 12, 1913, and left on March 28, 1933, explaining that he no longer desired to be associated with Prussia's government at that time.
- Einstein accepted the University of Manchester's doctorate of science degree on June 9, 1921; on that same date, he also delivered a public address in Manchester. What is more, on the same date, he got The Copley Medal from the Royal Society – truly putting cap to an extraordinary academic career 19-21!
- He received the society’s highest award, the Gold Medal, in 1926, for services to theoretical physics. Planck gave the medal of the German Physical Society Berlin to Einstein in 1929.
- Einstein was awarded the Prix Jules Janssen in 1931, while he delivered his Josiah Willard Gibbs lecture in 1934. To celebrate the World Year of Physics, which was observed on the occasion of the tercentenary of its publication, as declared by the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics, in honor of 100 years since publication…the year 2005 had been declared the World Year of Physics.
III. 7 Things that you can learn from Albert Einstein IQ
1. Follow Your Curiosity
“I have no special talent. I am only passionately curious”
Einstein wanted to convey through this quote that curiosity should be the cornerstone for every life decision. Follow your curiosity; no matter its source - and let it deepen over time! That distinguishes us from ordinary people: exploring areas no one had expected before discovering miracles we never suspected could exist so quickly! Keep exploring your vision, gathering all available data - you will be astounded at how extraordinary your life will become by adhering to curiosity!
2. Perseverance Is Priceless
Persistence was key in their significant discoveries, as every problem has at least one solution if we persist with finding it. Therefore, by building perseverance into your character, you can always overcome anything along your journey, such as vision loss if it arises; don't give up trying to solve problems as they may come your way!
3. Make Mistakes
"A person who never erred never ventured into novel territory."
Make mistakes, and you will follow Einstein's path" doesn't imply one particular interpretation; rather, it implies we must face our fears and unknowns head-on - whether that means moving to Alaska to find employment there or staying put here in Chicago without ever experiencing what life would be like in Alaska if that's our preference. Don't fear making errors: that separates successful from unsuccessful people; without daring to try something different or risk being incorrect, you won't ever learn how to address any weaknesses you might possess!
4. Create Value
“Strive not to be a success, but rather to be of value.”
Most people approach success inaccurately; success doesn't just refer to having wealth and running an automated company without our involvement; success means taking one step at a time towards creating things we will appreciate while building and sustaining them.
5. Knowledge Comes From Experience
"Knowledge is not information. Experience is the only source of knowledge."
Experience is easily discerned when we witness someone acting appropriately and competently under any given circumstance. It does not possess extensive knowledge in that area due to reading books or having access to extensive libraries at home; rather, they've encountered similar scenarios throughout their experience. Following suit with number 3, try to fail as often as possible to learn about alternative approaches to something; that way, experience is gained.

6. Learn The Rules And Play Better
Life entails learning the rules of the game, whether consciously or subconsciously. For instance, one would have to be persistent, conserve energy effectively, and accumulate experience fast enough to stay competitive with everyone. There is no requirement for you to go in one 'right’ way or follow someone 'successful’; full understanding of the rules of a game makes it possible for you to challenge or change them in order to play the best version of that particular sport.
7. The Imagination Is Powerful
Sometimes, it may feel complex to make decisions in life, but imagination serves us well by helping us make better ones.
WHAT IS YOUR IQ?
This IQ Test will help you test your IQ accurately
IQ Comparison with other Celebrities:
Albert Einstein
IQ 190
vs
IQ comparison with Albert Einstein
Maybe you are interested

